RFID asset tracking takes your equipment management, monitoring and other operations to the next level. If you're looking for a better way to manage your inventory, RFID asset tracking technology can help. The technology collects data about your assets that can be used to optimise asset usage and better manage inventory.
However, before you can use the data you collect, you must have a plan for using it. Otherwise, you will be left with a pile of numbers. But don't worry, with the right use of these systems, you will see a significant improvement in the efficiency of your business.
What is RFID asset tracking?
RFID asset tracking refers to the process by which you document all of your company's physical assets. RFID asset tracking technology automates the manual processes of asset management. It brings significant labor savings. Significantly reduces time, energy and costs.
Asset tracking RFID technology is a system that your company can implement to gain better control over your critical tools and equipment.
With asset tracking, your company can:
- Simultaneous view of the assets you own and their location
- Ability to monitor who is responsible for critical assets
- Tracking asset movements
- Search for lost or misplaced assets
- Maximising stock accuracy
All of these features ultimately streamline the day-to-day operations of your business and prevent the loss and theft of assets.
The importance of RFID asset tracking
While several options are available to streamline the process of RFID asset tracking, there is one tracking technology that offers full efficiency in the most cost-effective way. RFID asset tracking technology stands for 'Radio Frequency Identification', a technology that works via radio waves.
In its simplest form, RFID asset tracking is a way to automate the process of managing and locating physical assets. It works by uploading an RFID tag with the data and attaching it to a related entity. This data can include name, condition, quantity and location.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, we have become more and more accustomed to the idea of accessing things or doing things without having to touch things. And one of those technologies that helps us do things quickly without having to touch anything is asset tracking RFID.
How does RFID work Asset Tracking?
Regardless of the industry used, the basic principles of how an RFID tracking system works are the same. RFID tags are physically attached to your valuable assets. RFID readers are tailored to your business environment and strategically placed to 'read' the signals sent by RFID tags. They are transmitted to our RFID asset tracking software and the data is processed. An intuitive user interface allows you to track and find specific assets from a laptop on site, remotely through your web browser or even on the go with your mobile device.
The components of the system are as follows:
- RFID tags (passive, active or semi-passive)
- One antenna
- RFID reader
- A computer database equipped with RFID asset tracking software
RFID asset tracking process
- Data is stored in an RFID tag with a unique electronic product code and attached to an asset
- An antenna identifies the signal from a nearby RFID tag
- An RFID reader connects wirelessly to the antenna and receives data stored on the RFID tag.
- The RFID reader then transmits the data to an RFID asset tracking database where it is stored, evaluated and processed.
RFID readers
It uses internal antennas to emit radio waves to retrieve signals from RFID tags (or, connects wirelessly to the antenna to receive information in more complex systems). Readers are usually mobile, which means users can take them anywhere, but they can also be mounted (e.g. on a tall pole that allows them to see a large part of a warehouse). RFID readers evaluate information in real time and can transmit the data to a software system where it is stored and referenced as needed.
Definition of RFID tags
RFID tags are a type of RFID asset tracking system that uses intelligent barcodes to identify items. RFID tags use radio frequency technology. These radio waves transmit data from the tag to a reader and then the information to an RFID computer programme. An RFID tag can also be called an RFID chip.
RFID tags are attached to each asset and continuously transmit data to an antenna (integrated or separate from the reader). RFID tags can store a wealth of information, from a single serial number to pages of associated data ranging from date of manufacture, condition and temperature to serial number, location, movements and storage requirements. Anything that is important to the organisation and can be digitised can be loaded onto a tag for processing.
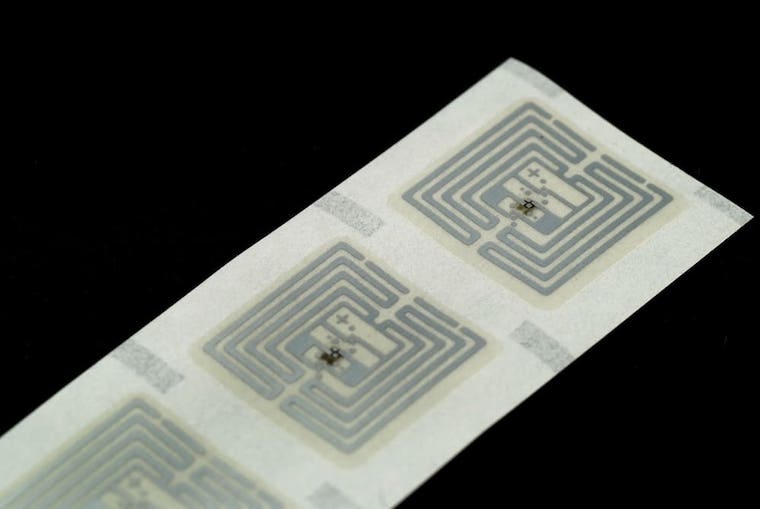
There are three main types of RFID tags
- Active RFID: Active RFID asset tracking has its own power source, usually a battery. They are battery-powered tags that continuously transmit signals. It is often used in processes to monitor assets in real time, such as vehicle tracking and charging. Depending on the frequency of the tag, active RFID asset tracking has a signal range of approximately up to 150 metres. It is also generally more expensive than passive RFID asset tracking.
- Passive RFID: Unlike traditional item tracking, passive RFID asset tracking lets you add and remove RFID readers as needed. You can track items more efficiently by adding more RFID readers. It has no internal power supply and is powered by an RFID reader or antenna. It is widely used for inventory tracking, supply chain management and access control. It has a shorter signal range than active RFID asset tracking. It is also smaller, lighter and has a longer lifetime than active RFID asset tracking. It is also a cheaper option than active RFID asset tracking.
- Semi-passive RFID tag: Is a mixture of both that has internal batteries as well as an antenna and an RFID chip. It has a low signal range compared to the active RFID tag. The addition of a battery allows for additional features such as real-time monitoring and sensors. It is used in close proximity to the RFID reader. It is often used for environmental and condition monitoring such as temperature-controlled switching.
Why companies choose RFID for inventory tracking
Today, companies are focused on increasing operational efficiency to stay ahead of the competition. Asset tracking systems with RFID are used in many major industries, including logistics, automotive, manufacturing, retail and construction. The use of asset tracking RFID technology enables companies to automatically track the movement of goods.
The data collection process is also automated, allowing companies to receive accurate, real-time updates directly to an RFID asset tracking system. From here, asset managers can monitor stock levels, monitor the supply chain and even identify costly delays in operations. This eliminates the need for manual monitoring methods such as spreadsheets, effectively reducing staff time and human intervention.
Work smarter with the RFID Asset Tracking System
RFID is not only popular in asset management, but is also taking control of employee performance. The new passive RFID-enabled system is designed to monitor employee attendance, productivity, workflow and more. For example, you can measure the time it takes a mechanic to repair a service tool.
You can achieve this by using RFID-based employee badges. The RFID performance tracking system can be seamlessly integrated with the RFID asset tracking system and increase the overall efficiency of your business. Investing in a versatile RFID asset tracking technology system allows you to work smarter and take control of your assets, workflows and employees.